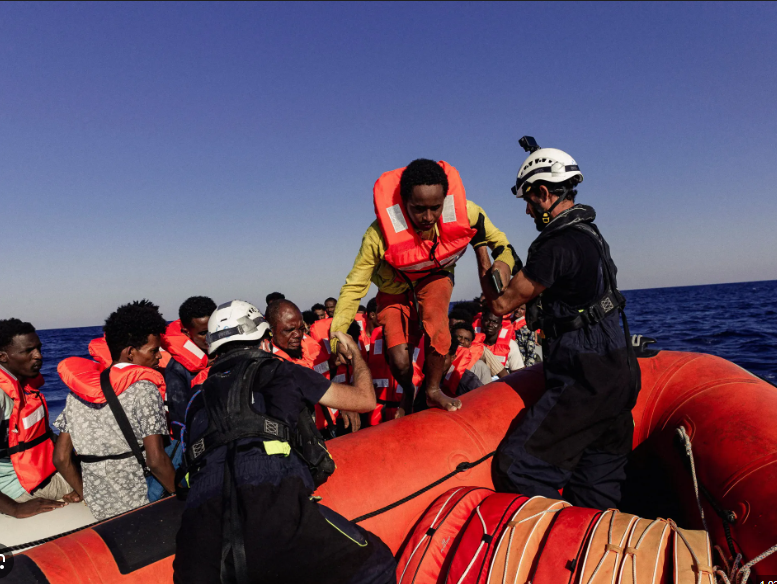
Italy, a country renowned for its rich history, beautiful landscapes, and delicious cuisine, has a complex relationship with immigration. The question of whether Italians like immigrants is nuanced and varies widely depending on several factors, including geography, local culture, and political leanings.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Regional Differences: North vs. South
One of the most significant factors influencing attitudes toward immigrants in Italy is geography. There is a noticeable divide between the northern and southern regions of the country.
Northern Italy:
- The further north you go, the more likely you are to encounter xenophobic and closed-minded attitudes. This region, led predominantly by far-right parties, tends to be less welcoming to immigrants, particularly those from Africa.
- The Northern League, a prominent far-right party, has historically advocated for the separation of Northern Italy from the rest of the country. Discrimination against southerners is still prevalent in regions like Veneto and Lombardy.
- Despite these challenges, the North offers more job opportunities due to its economic connections with Central Europe. This economic advantage forces many immigrants to move north despite the social difficulties they might face.
Southern Italy:
- In contrast, Southern Italy is generally more amiable and immigrants often find it easier to assimilate. The people in the South are known for their hospitality and open-mindedness.
- Southern regions do, however, face higher unemployment rates, making it harder for both locals and immigrants to find work.
Urban vs. Rural Areas
Another critical factor is the difference between urban and rural areas.
- Cities: Major cities in Italy, such as Rome, Milan, and Naples, are more accustomed to seeing diversity and tend to be more accepting of immigrants. The cosmopolitan nature of these cities means that immigrants can blend in more easily and find communities of people from similar backgrounds.
- Small Municipalities: In smaller towns and villages, residents may initially be more wary of newcomers. These areas are less diverse and less experienced in dealing with immigrants, which can lead to a more cautious or even hostile reception.
Political Influences
Italy’s political landscape significantly impacts attitudes towards immigrants.
- Northern Regions: Dominated by far-right parties, these regions often have stricter immigration policies and a higher incidence of xenophobia.
- Central and Southern Regions: Areas like Tuscany and Emilia Romagna, which lean more towards left-wing politics, generally exhibit lower levels of racism. These regions offer a good balance of economic opportunity and social acceptance, making them a preferable choice for immigrants.
Social and Economic Factors
- Economic Opportunities: The availability of jobs is a crucial factor. Immigrants tend to move to regions with better job prospects, even if it means facing social challenges. Northern Italy, despite its less welcoming attitude, attracts many immigrants due to its stronger economy.
- Social Integration: The ease of social integration varies. In the South and certain central regions, immigrants may find it easier to build social networks and integrate into the community.
Practical Advice for Immigrants
- Consider Central Regions: For those seeking a balance between economic opportunity and social acceptance, regions like Tuscany and Emilia Romagna are ideal. These areas offer decent job prospects and a relatively welcoming environment.
- Long-term Strategy: Some immigrants might choose to start in the North to take advantage of job opportunities and then move to the South or Central regions once they have established themselves economically.
 Categories
Categories
 Discover Italy
Discover Italy
 Life
Life
 Travel
Travel
 Nature
Nature
 Explore Food
Explore Food